An Air Brake System is a type of braking system that uses compressed air to apply pressure in order to stop the vehicle. Air brakes are also known as pneumatic brakes. The first air brake was invented by George Westinghouse, he introduced this type of brake for use in trains.
Air brakes are widely used in heavy vehicles like trucks and buses because they are heavy in weight and they need more effort on the brake pedal to stop them. The air brake is good for comfortable braking as it has high potential energy and does not require much effort to push the brake pedal. They are not used in small vehicles like cars because they are lightweight and the space is less to install an air brake. For cars, hydraulic brakes are good as they require less space to install.
Air Brake Components
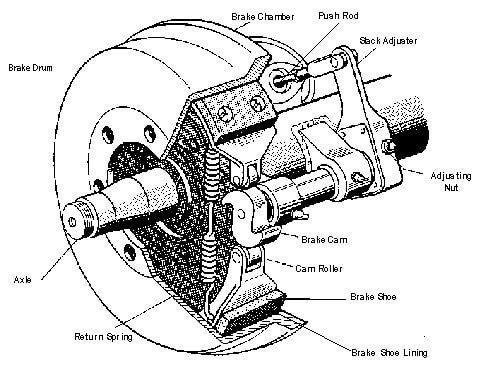
A simple air brake system consists of an air compressor, a brake valve, a series of brake chambers, an unloader valve, a pressure gauge, and a safety valve. All these air brake system components are connected by lines of tubing.
Some other air braking systems may have additional components such as a stop light switch, a low-pressure indicator, an air supply valve to supply air for tyre inflation, a quick release valve to release air quickly from the front brake chambers when the pedal is released, a limiting valve for limiting the maximum pressure in the front brake chambers and a relay valve to help in quick admission and release of air from rear brake chambers.
The main components of Air Brakes are:
- The Filter filters the air by removing/blocking dust particles and allowing clean air into the system. The filtered air is sent to the air compressor.
- Then, the Compressor takes air through the filter and then compresses the air.
- Reservoir stores compressed air which is used for the braking system.
- The Unloader valve, situated at the compressor opens when the compressor pressure switch trips to the OFF position.
- Then, the Brake valve opens when the brakes are applied by extending lines of tubing.
Air Brakes Working (Road Vehicles)
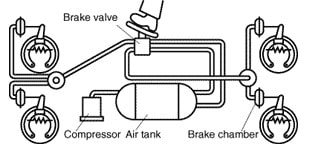
First, the compressor takes air from the atmosphere through an air filter that filters the air and it gets compressed. Then this compressed air is sent to the reservoir/air tank through the unloader valve, which opens at a predefined reservoir pressure and is connected to the brake valve. The lines of tubing from the brake valve extend to the front and rear brake chambers.
The compressed air is supplied to brake chambers placed at each wheel, through the brake valve which is controlled by the driver (the intensity of braking according to the requirement).
When the brake pedal is pressed, pressure in the reservoir drops which then pushes the brake pad against the brake drum and the braking action occurs. The vehicle slows down or stops according to the pressure applied.
When the brake pedal is released, the unloader valve gets closed and there is no pressure on the brake pads.
Additionally, the compressed air available inside the air tank is also used for operating additional assemblies like horns, windshield wipers, etc.
Application
- It is used in heavy vehicles as they require more braking force. Air Brakes were also used in small cars before but were replaced with drum brakes and disc brakes as there is less space for installing air brakes.
- They are used in trucks buses, trains and locomotives.
Advantages
- The air braking system is cleaner.
- Air is freely available so no cost for air.
- Ease of use and maintenance.
- Safe and explosion proof.
- Reserved compressed air can be used in multiple ways.
Disadvantages
- The air can leak very easily.
- When the air brakes are applied there is a noise produced due to the air. The noise is also produced while changing the pressure from the compressor.
- It does not work underwater and under extreme temperatures.
- It is harder to find leaks in air brakes than in hydraulic brakes. In the case of hydraulic brakes, the fluid can be seen over the leakage area.
- Weird noise of air escape in buses and trucks while running.










Leave a Reply
View Comments